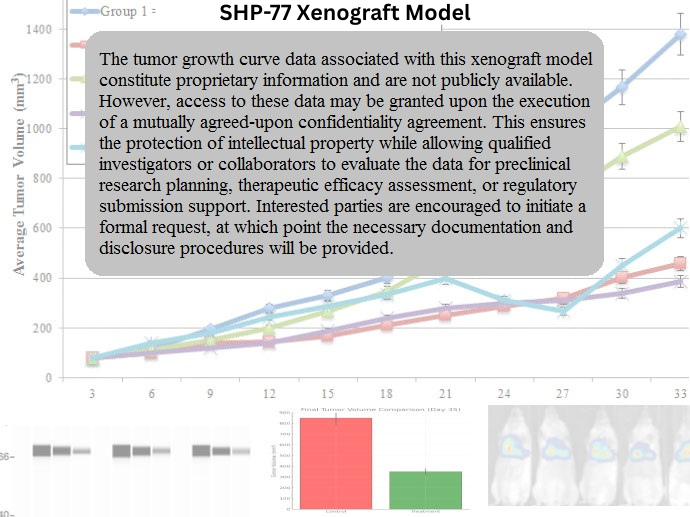
SHP-77 Xenograft Model Overview
The SHP-77 xenograft model is derived from a human small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC) cell line originally established from the pleural effusion of a patient with advanced-stage disease. As a model of non-classical or variant SCLC, SHP-77 exhibits distinct phenotypic and molecular characteristics compared to conventional neuroendocrine SCLC cell lines such as NCI-H69 or NCI-H82. It serves as a unique platform for studying atypical SCLC biology and testing therapeutic strategies aimed at non-neuroendocrine or mixed phenotype tumors. The SHP-77 xenograft is particularly valuable for research focused on tumor heterogeneity, therapeutic resistance, and lineage plasticity within small cell lung cancer subtypes.
Request a Custom Quote for SHP‑77 Xenograft ModelBiological and Molecular Characteristics
SHP-77 cells display moderate neuroendocrine differentiation with partial expression of neuroendocrine markers, including synaptophysin and neuron-specific enolase (NSE), but lower levels of chromogranin A compared to classical SCLC lines. Importantly, this cell line retains a more epithelial-like morphology and demonstrates higher adherence in culture, distinguishing it from other floating SCLC cell lines. Genomic studies indicate mutations in TP53, partial inactivation of RB1, and aberrant expression of genes associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and DNA repair. SHP-77 also exhibits responsiveness to cAMP signaling modulation and features an intermediate proliferative index.
| Characteristic | SHP-77 Cell Line Profile |
|---|---|
| Tumor Origin | Small cell lung carcinoma (variant phenotype) |
| Neuroendocrine Markers | Synaptophysin⁺, NSE⁺, Chromogranin A (low/variable) |
| Growth Morphology | Adherent monolayer |
| Key Genetic Alterations | TP53⁺/⁻, RB1 partial loss, EMT gene expression |
| Ki-67 Proliferation Index | Intermediate (~50–60%) |
In Vivo Model Development and Tumorigenicity
To establish the SHP-77 xenograft model, cultured cells are injected subcutaneously into immunodeficient mice, typically athymic nude or NOD/SCID strains. Tumor formation is consistent, though the latency period may be slightly longer than that of classical SCLC models. Tumors display a moderate growth rate and maintain histological features representative of the parent cell line. Due to its distinct biology, the SHP-77 model enables investigation into slower-growing or treatment-resistant SCLC variants, and it can support extended-duration therapeutic trials for cytostatic and targeted agents.
Request a Custom Quote for SHP‑77 Xenograft ModelHistopathology and Immunohistochemical Profile
Histologically, SHP-77 xenografts exhibit a heterogeneous cellular population with both small round cells and spindle-shaped elements. The tumors demonstrate partial neuroendocrine morphology, with focal expression of synaptophysin and moderate NSE staining. Chromogranin A expression is typically reduced or patchy, and the Ki-67 index is lower than in classical SCLC models, indicating an intermediate proliferative potential. The histopathology reflects the non-classical nature of this variant SCLC model and offers valuable insight into the phenotypic diversity of small cell lung tumors.
Preclinical Applications and Drug Response
SHP-77 xenografts are used to assess the efficacy of agents targeting atypical or treatment-refractory SCLC subtypes. The model has shown variable sensitivity to platinum-based chemotherapy and is well-suited for evaluating targeted agents that modulate EMT, cAMP signaling, or histone methylation. It also enables investigation of novel therapeutic combinations designed to overcome partial resistance mechanisms and improve efficacy in variant SCLC. The SHP-77 xenograft model is increasingly relevant for testing therapies that aim to exploit molecular vulnerabilities unique to non-neuroendocrine or hybrid small cell phenotypes.
Request This Model
The SHP-77 xenograft model offers a distinctive and clinically relevant approach to preclinical studies involving variant small cell lung cancer. To request tumor growth kinetics, histological validation, or customized study designs using this model, please contact us directly.
Request a Custom Quote for SHP‑77 Xenograft Model