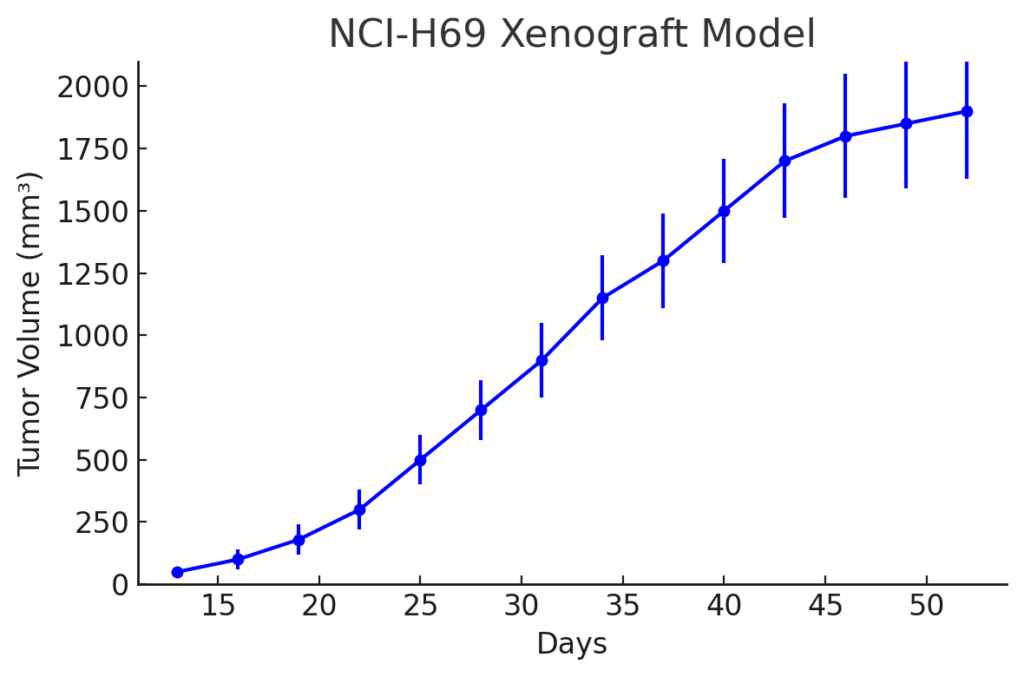
NCI-H69 Xenograft Model Overview
The NCI-H69 xenograft model is derived from a human small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC) and is one of the most widely used preclinical platforms for investigating high-grade neuroendocrine tumors of pulmonary origin. Established from a lymph node metastasis, the NCI-H69 cell line retains key molecular and phenotypic features of classic SCLC, including neuroendocrine differentiation, rapid proliferation, and sensitivity to first-line chemotherapeutics. This model offers a well-characterized system for studying tumor progression, chemoresistance, and evaluating emerging treatment modalities such as DNA-damaging agents, epigenetic drugs, and immunotherapy in SCLC.
Request a Custom Quote for NCI‑H69 Xenograft ModelBiological and Molecular Characteristics
NCI-H69 cells exhibit round morphology with scant cytoplasm and form floating aggregates in suspension culture. The line expresses hallmark neuroendocrine markers such as neuron-specific enolase (NSE), chromogranin A, and synaptophysin, reflecting its neuroendocrine tumor origin. Genomic analyses reveal loss-of-function mutations in both TP53 and RB1, which are defining molecular events in SCLC tumorigenesis. Additionally, NCI-H69 cells have high c-MYC expression and exhibit deregulated expression of BCL2, contributing to enhanced survival and drug resistance. The lack of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I expression aligns with the immune-evasive phenotype often observed in aggressive SCLC subtypes.
| Characteristic | NCI-H69 Cell Line Profile |
|---|---|
| Tumor Type | Small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC) |
| TP53 and RB1 Status | Mutated (inactivated) |
| Neuroendocrine Markers | NSE⁺, Chromogranin A⁺, Synaptophysin⁺ |
| c-MYC and BCL2 Expression | Elevated |
| MHC Class I | Low/Absent |
In Vivo Model Development and Tumorigenicity
NCI-H69 xenografts are established through subcutaneous injection of cultured cells into immunocompromised mice such as athymic nude or NOD/SCID strains. Tumors typically appear within 10–14 days and grow rapidly, with measurable volumes suitable for pharmacologic intervention by three weeks post-injection. Xenografts derived from NCI-H69 cells exhibit uniform growth kinetics and reproducible histological features, enabling consistency across efficacy studies. The model’s responsiveness to DNA-damaging agents and apoptotic modulators supports its use in testing both conventional and novel therapeutic classes.
Request a Custom Quote for NCI‑H69 Xenograft ModelHistopathology and Immunohistochemical Profile
Histologically, NCI-H69 xenografts are composed of densely packed small round cells with high nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratios, finely granular chromatin, and frequent mitotic figures. Tumors display extensive regions of necrosis due to their rapid growth and limited vascularization. Immunohistochemical staining confirms strong positivity for neuroendocrine differentiation markers including chromogranin A and synaptophysin, while Ki-67 indices consistently exceed 80%, highlighting the model’s highly proliferative nature. Absence of MHC class I staining and low infiltration by immune effector cells are consistent with the immunosuppressive environment associated with SCLC.
Preclinical Applications and Drug Response
The NCI-H69 xenograft model has been extensively utilized for evaluating standard-of-care chemotherapeutics such as cisplatin, carboplatin, and etoposide, which remain frontline treatments in SCLC. Its molecular profile and rapid tumor kinetics also make it suitable for assessing BCL2 inhibitors, PARP inhibitors, and HDAC inhibitors, particularly in the context of MYC-driven tumor biology. The model is increasingly employed in immunotherapy research to evaluate strategies aimed at restoring antigen presentation or reversing immune escape mechanisms. Overall, NCI-H69 provides a clinically relevant and experimentally tractable model for investigating drug resistance, neuroendocrine plasticity, and therapeutic vulnerabilities in SCLC.
Request This Model
To include the NCI-H69 xenograft model in your small cell lung cancer research pipeline, contact us to obtain validated tumor growth data, histological profiles, and expert guidance for customized in vivo study design.
Request a Custom Quote for NCI‑H69 Xenograft Model